路由
一、Angular中的路由
在创建项目的时候使用--routing参数可以使得项目自带路由模块。
ng new angularRouter --routing
生成的项目中有一个app-routing.module.ts 文件就是路由配置文件。
为了测试方便,创建Home和Goods,Detail页面:
ng g c pages/Home
ng g c pages/Goods
ng g c pages/Detail
路由配置:
import { HomeComponent } from './pages/home/home.component';
import { GoodsComponent } from './pages/goods/goods.component';
import { DetailComponent } from './pages/detail/detail.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/home',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
{
path: 'home',
component: HomeComponent,
children : [
{
path : "a",
component : AComponent
}
]
},
{
path: 'goods',
component: GoodsComponent
},
{
path: 'detail',
component: DetailComponent
},
// 路由不存在时匹配
{
path: '**',
component: PageNotFoundComponent
}
];
注意:
1、路径不加
/2、路由不存在时匹配
**跳转到404页面。3、重定位
redirectTo: '/home',4、pathmatch中的“full”,代表的是当path中是空时,redirectTo会转向主页的路径上
二、路由跳转
1、标签跳转
在主组件中点击a标签跳转到Home组件和Goods组件。
<!-- app.component.html -->
<a [routerLink]="[ '/' ]">首页</a>
<a [routerLink]="[ '/goods' ]">商品详情页</a>
路由跳转:
[routerLink]="[ '/' ]第一个[]表示routerLink是可变的,路由也是数组,是为了在数组的第二个参数添加参数,比如跳转到详情页需要传入商品id。
2、编程式导航
在控制器(ts文件的类中)中,通过js跳转需要进行两步:
第一步: 在构造函数中声明 Router实例
例如: constructor(private xxx:Router){}
第二部 调用Router实例的navigate()方法即可(注意,该方法接收的参数为数组类型)
例如: this.xxx.navigate(["/home"]) 跳转到首页
示例:
/*app.component.html*/
<button (click)="goPage('/')">首页</button>
<button (click)="goPage('/goods')">商品列表</button>
/*app.component.ts*/
import { Router } from "@angular/router";
constructor(private router: Router) { } // 注意导入Router
goPage(path) {
this.router.navigate([path]); // 是个数组
}
三、路由传参
1、问号传参
goods页点击商品跳转到detail页面,商品id由地址栏传递:
<!-- goods.component.html -->
<div>
<ul>
<li
*ngFor="let goods of list"
[routerLink]="[ '/detail']"
[queryParams]="{goodsID:goods.id}"
>
<p>商品名:{{goods.name}}</p>
<p>价格:{{goods.price}}</p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
给元素添加属性 queryParams即可传递想要的数据
详情页detail从地址栏获取id:
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
export class DetailComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(
private ar: ActivatedRoute
) { }
ngOnInit() {
let id = this.ar.snapshot.queryParams['goodsID'];
console.log(id);
}
}
给当前组件注入 ActivatedRoute,通过注入的服务实例来获取参数
注意:直接打印 this.ar.snapshot.queryParams 是一个对象,但是只能使用数组的方式获取。
2、路径传参
首先需要修改路由配置:
{
path: 'detail/:goodsID',
component: DetailComponent
}
<!-- goods.component.html -->
<div>
<ul>
<li
*ngFor="let goods of list"
[routerLink]="[ '/detail', goods.id]">
<p>商品名:{{goods.name}}</p>
<p>价格:{{goods.price}}</p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
参数通过routerLink属性值的数组第二个元素进行传参
详情页获取id:
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
export class DetailComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(
private ar: ActivatedRoute
) { }
ngOnInit() {
let id = this.ar.snapshot.params['goodsID'];
console.log(id);
}
}
获取的方式和问号传参唯一的区别:
需要通过 this.xxx.snapshot.params['goodsID']来获取数据。
当从详情页跳转到详情页的时候,由于详情页组件没有进行组件的卸载和加载,所以不能使用上面参数快照的方式进行,而需要采用参数订阅的方式:
ngOnInit() {
// let id = this.ar.snapshot.params['goodsID'];
this.ar.params.subscribe(params => {
console.log(params['goodsID']);
})
}
四、辅助路由(多视图路由)
与vue等框架的区别在于,angular的对视图路由互相是独立的,A视图更换路由不会改变B视图的显示,反之亦然。
在主组件的html设置显示主路由和辅助路由。
<!--app.component.html-->
<button (click)="goPage('/home')">首页</button>
<button (click)="goPage('/goods')">商品列表</button>
<a [routerLink]="[ {outlets:{box:'a'}} ]">辅助路由 1</a>
<a [routerLink]="[ {outlets:{box:'b'}} ]">辅助路由 2</a>
<div class="panel">
<div class="main">
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
<div class="box">
<router-outlet name="box"></router-outlet>
</div>
</div>
辅助路由定义一个name属性box。
修改路由:
import { AComponent } from './components/a/a.component';
import { BComponent } from './components/b/b.component';
const routes: Routes = [
//...
{
path: 'a',
component: AComponent,
outlet: 'box'
},
{
path: 'b',
component: BComponent,
outlet: 'box'
},
//...
];
注意属性
outlet: 'box'表示组件渲染的是名字为box的路由。
然后点击a标签进行辅助路由跳转:
<a [routerLink]="[ {outlets:{box:'a'}} ]">辅助路由 1</a>
<a [routerLink]="[ {outlets:{box:'b'}} ]">辅助路由 2</a>
当点击a标签的时候,将box替换为a组件或者b组件。
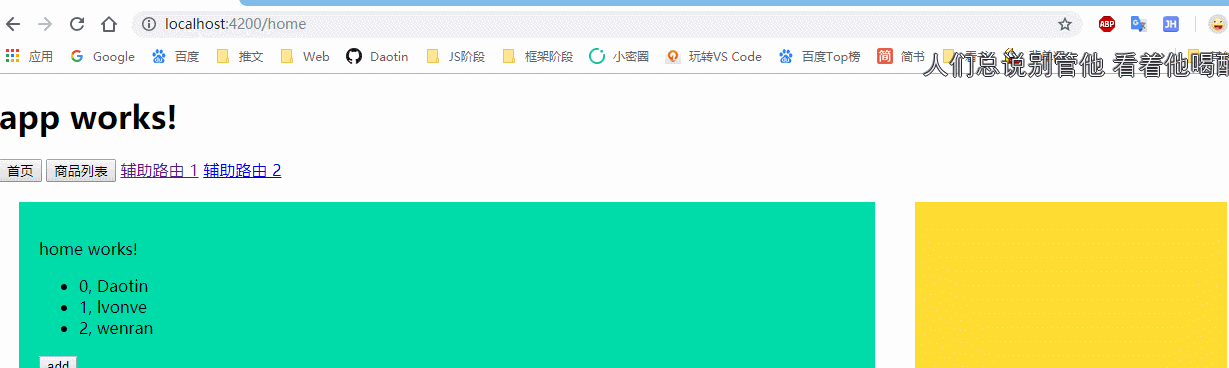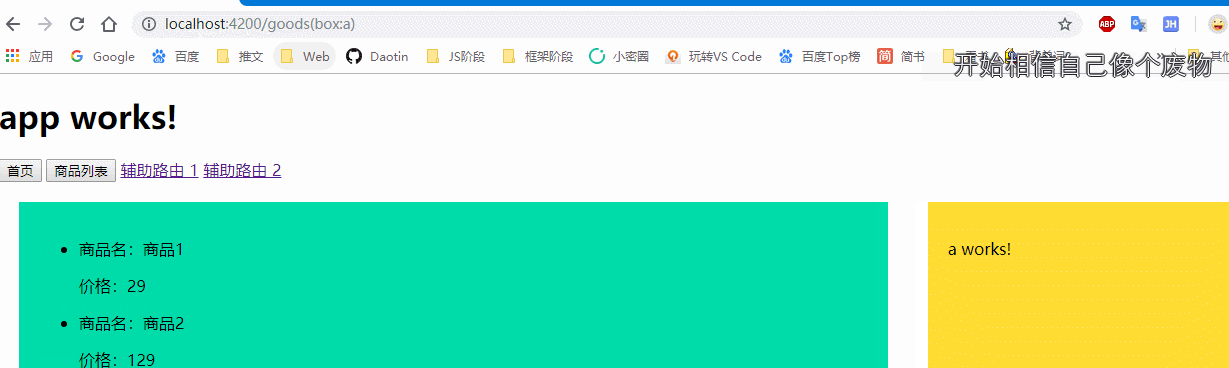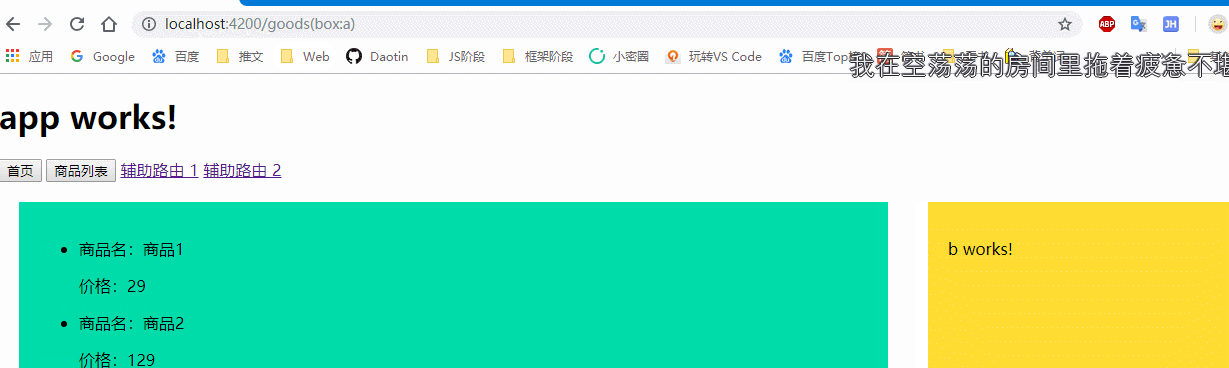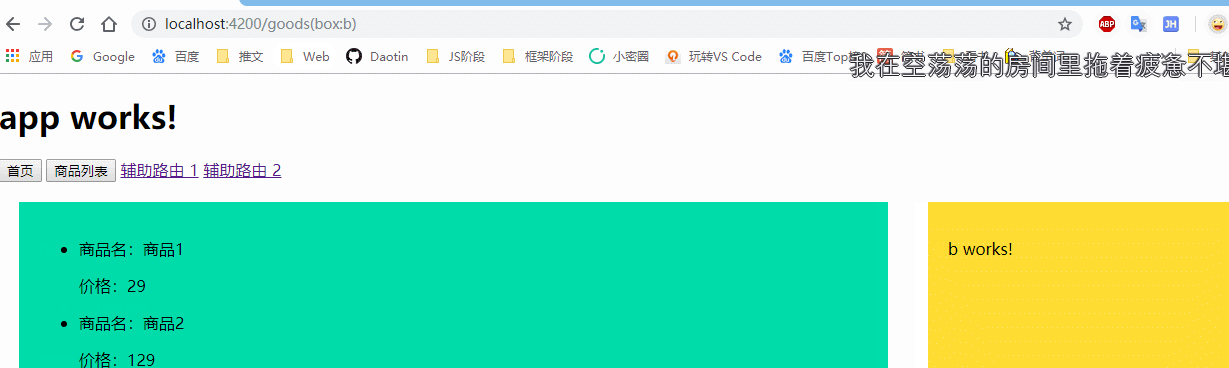
可以看到:当点击主路由时不影响辅助路由的跳转,点击辅助路由时不影响主路由的跳转。并且辅助路由会以括号的形式显示在地址栏上。
五、路由守卫
常见的由进入的路由守卫和离开的路由守卫。本质上来说,路由守卫就是类。
在guards目录下新建一个进入路由守卫和一个离开路由守卫。路由守卫其实就是一个类,所以:
ng g cl guards/Enter
ng g cl guards/Leave
1、编写进入守卫模块
import { CanActivate } from "@angular/router";
export class Enter implements CanActivate {
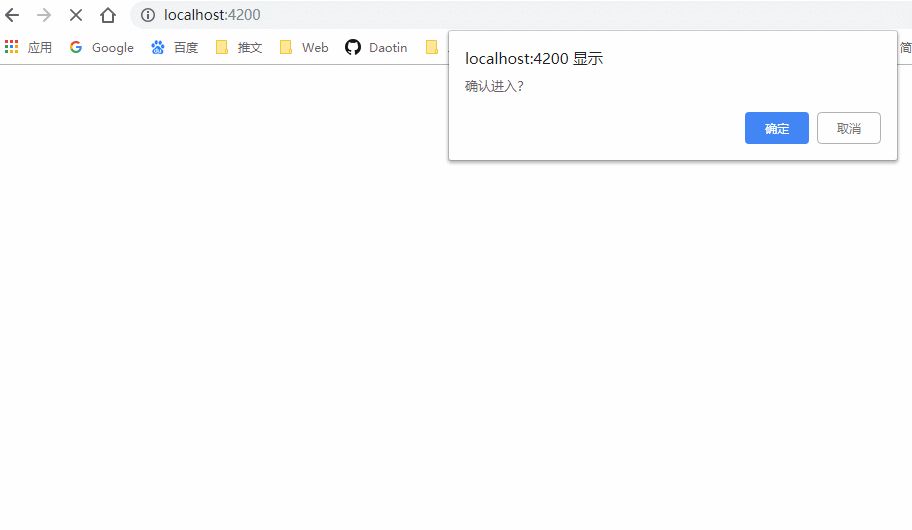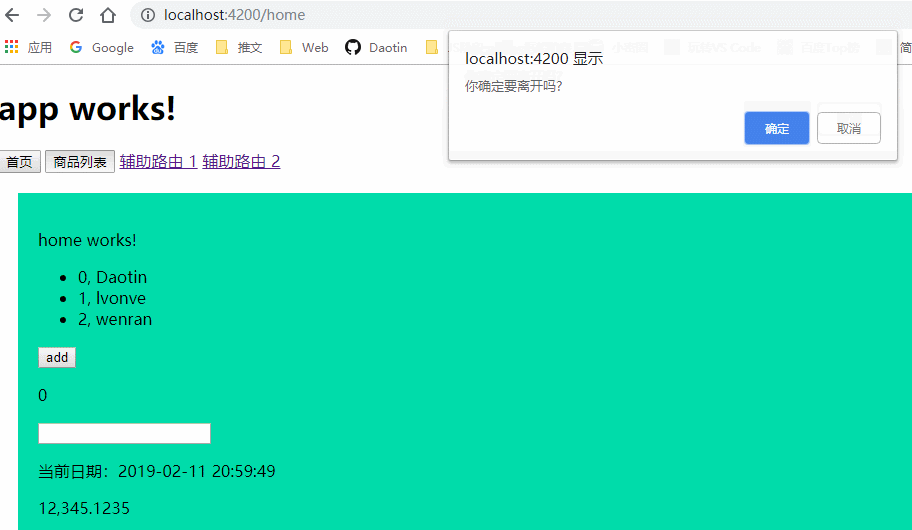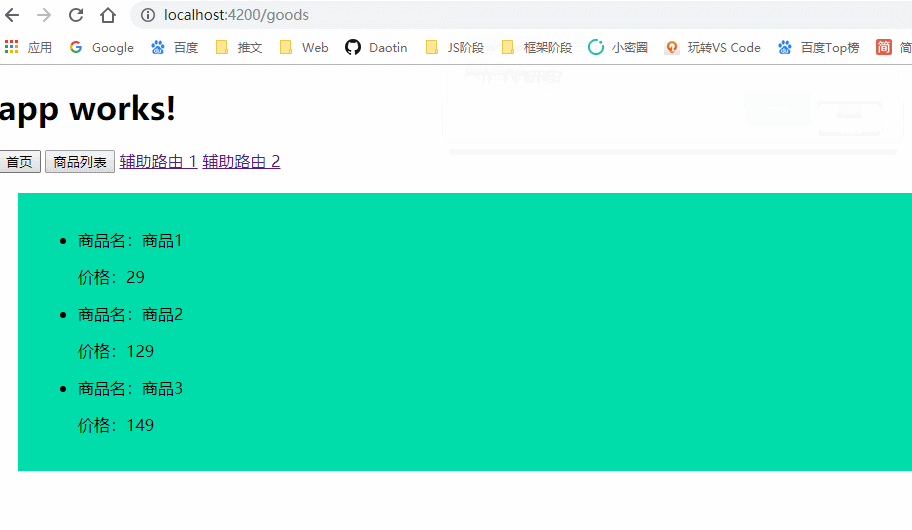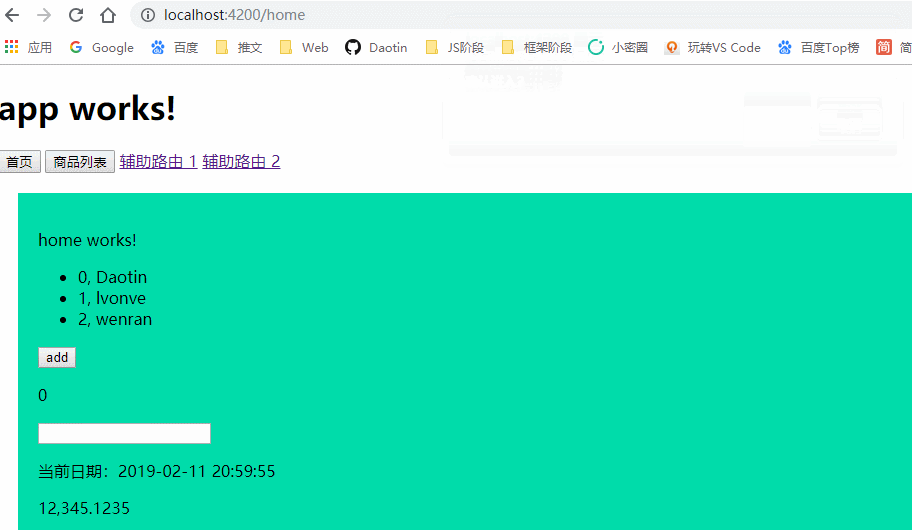
canActivate(): boolean {
// 返回true运行跳转,返回false禁止跳转
return confirm('确认进入?');
}
}
进入的路由守卫需要实现接口: CanActivate
2、将其注入到路由模块的providers属性中
providers: [Enter]
3、在需要监控的路由配置上添加对应的路由守卫。
{
path: 'home',
component: HomeComponent,
canActivate: [Enter]
},
{
path: 'goods',
component: GoodsComponent,
canActivate: [Enter]
},
如果有多个路由守卫的话,路由守卫会依次验证。
离开守卫:
离开的路由守卫需要实现接口 :CanDeactivate (除了要实现接口,还得定义泛型),其他都是相同的。
import { CanDeactivate } from "@angular/router";
import { GoodsComponent } from "app/pages/goods/goods.component";
export class Leave implements CanDeactivate<GoodsComponent> {
canDeactivate(): boolean {
return confirm("你确定要离开吗?")
}
}
注意:进入守卫和离开守卫的区别:
离开守卫除了要实现接口,还得定义泛型。
注入:
providers: [Enter,Leave]
添加相应的路由守卫:
{
path: 'home',
component: HomeComponent,
canActivate: [Enter],
canDeactivate: [Leave]
},
{
path: 'goods',
component: GoodsComponent,
canActivate: [Enter],
canDeactivate: [Leave]
},